
#SPIN ECHO SEQUENCE DIAGRAM SERIES#
This sequence is characterized by a series of rapidly applied 180° rephasing pulses and multiple echoes, changing the phase encoding gradient for each echo. (FSE) In the pulse sequence timing diagram, a fast spin echo sequence with an echo train length of 3 is illustrated. MRI Reimbursement - Mass Spectrometry - Shielding - Manufacturers - MRI Technician and Technologist Schools - Services and Supplies See Depth Pulses, Volume Selective Excitation, Depth Resolved Spectroscopy. (DEPTH) A sequence with multiple RF pulses to enable acquiring data from only selected regions. Spin Echo Sequence for Spatial Localization Monday, 19 March 2012 by īrain MRI - Cochlear Implant - Fluorescence - Patient Information - Safety Products Thursday, 23 April 2009 by MRI techniques improve pulmonary embolism detection New MR sequence helps radiologists more accurately evaluate abnormalities of the uterus and ovaries Tuesday, 24 January 2006 by Magnetic resonance imaging See also Pulse Sequence Timing Diagram to find a description of the components. For this reason, spin echo sequences are more robust against e.g., susceptibility artifacts than gradient echo sequences. With spin echo imaging no T2* occurs, caused by the 180° refocusing pulse. T2 weighted: Long TE (greater than 60 ms) and long TR (greater than 1600 ms) T1 weighted: Short TE (10-20 ms) and short TR (300-600 ms) PD weighted: Short TE (20 ms) and long TR. In the simplest form of SE imaging, the pulse sequence has to be repeated as many times as the image has lines. The SE pulse sequence was devised in the early days of NMR days by Carr and Purcell and exists now in many forms: the multi echo pulse sequence using single or multislice acquisition, the fast spin echo (FSE/TSE) pulse sequence, echo planar imaging (EPI) pulse sequence and the gradient and spin echo (GRASE) pulse sequence all are basically spin echo sequences.
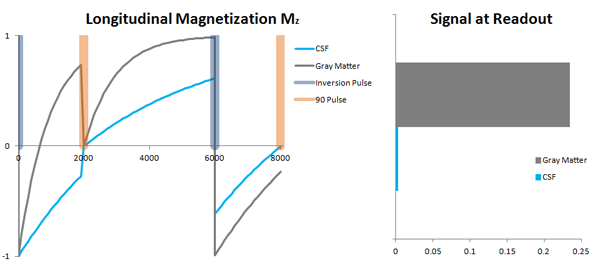
The recovery of the z-magnetization occurs with the T1 relaxation time and typically at a much slower rate than the T2-decay, because in general T1 is greater than T2 for living tissues and is in the range of 100-2000 ms.

The purpose of the 180° pulse is to rephase the spins, causing them to regain coherence and thereby to recover transverse magnetization, producing a spin echo. The following application of a 180° refocusing pulse (rotates the magnetization in the x-plane) generates signal echoes. The 90° excitation pulse rotates the longitudinal magnetization ( Mz) into the xy-plane and the dephasing of the transverse magnetization (Mxy) starts. In the pulse sequence timing diagram, the simplest form of a spin echo sequence is illustrated. It uses 90° radio frequency pulses to excite the magnetization and one or more 180° pulses to refocus the spins to generate signal echoes named spin echoes (SE). (SE) The most common pulse sequence used in MR imaging is based of the detection of a spin or Hahn echo. Searchterm ' Spin Echo Sequence' was also found in the following service: Result : Searchterm ' Spin Echo Sequence ' found in 2 terms and 27 definitions ġ - 5 (of 29) next Result Pages : 2 3 5 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
